Spatially Sparse Data Structures
note
Prerequisite: please read the Fields, Fields (advanced), and SNodes first.
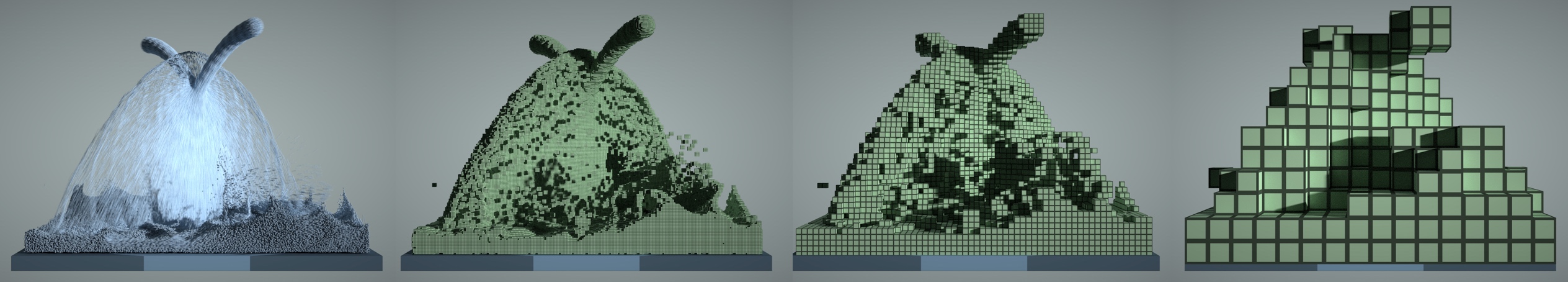 Figure: A 3D fluid simulation that uses both particles and grids. Left to right: particles, 1x1x1 voxels, 4x4x4 blocks, 16x16x16 blocks.
Figure: A 3D fluid simulation that uses both particles and grids. Left to right: particles, 1x1x1 voxels, 4x4x4 blocks, 16x16x16 blocks.
Motivation
In large-scale spatial computing, such as physical modelling, graphics, and 3D reconstruction, high-resolution 2D/3D grids are frequently required. However, if we employ dense data structures, these grids tend to consume a significant amount of memory space and processing (see field and field advanced). While a programmer may allocate large dense grids to store spatial data (particularly physical qualities such as a density or velocity field), they may only be interested in a tiny percentage of this dense grid because the remainder may be empty space (vacuum or air).
To illustrate this idea, the regions of interest in sparse grids shown below may only occupy a small fraction of the whole bounding box. If we can leverage such "spatial sparsity" and focus computation on the regions we care about, we will significantly save storage and computing power.

note
The key to leveraging spatial sparsity is replacing dense grids with sparse grids.
Sparse data structures are traditionally based on Quadtrees (2D) and Octrees (3D). Given that dereferencing pointers is relatively costly on modern computer architectures, Quadtrees and Octrees are less performance friendly than shallower trees with larger branching factors, such as VDB and SPGrid. In Taichi, you can compose data structures similar to VDB and SPGrid with SNodes. The advantages of Taichi spatially sparse data structures include:
- Access with indices, which just like accessing a dense data structure.
- Automatic parallelization when iterating.
- Automatic memory access optimization.
note
Backend compatibility: The LLVM-based backends (CPU/CUDA) offer the full functionality for performing computations on spatially sparse data structures. Using sparse data structures on the Metal backend is now deprecated. The support for Dynamic SNode has been removed in v1.3.0, and the support for Pointer/Bitmasked SNode will be removed in v1.4.0.
note
Sparse matrices are usually not implemented in Taichi via spatially sparse data structures. See sparse matrix instead.
Spatially sparse data structures in Taichi
Spatially sparse data structures in Taichi are composed of pointer, bitmasked, dynamic, and dense SNodes. A SNode tree merely composed of dense SNodes is not a spatially sparse data structure.
On a spatially sparse data structure, we consider a pixel, a voxel, or a grid node to be active if it is allocated and involved in the computation. The rest of the grid simply becomes inactive. In SNode terms, the activity of a leaf or intermediate cell is represented as a Boolean value. The activity value of a cell is True if and only if the cell is active. When writing to an inactive cell, Taichi automatically activates it. Taichi also provides manual manipulation of the activity of a cell: See Explicitly manipulating and querying sparsity.
note
Reading an inactive pixel returns zero.
Pointer SNode
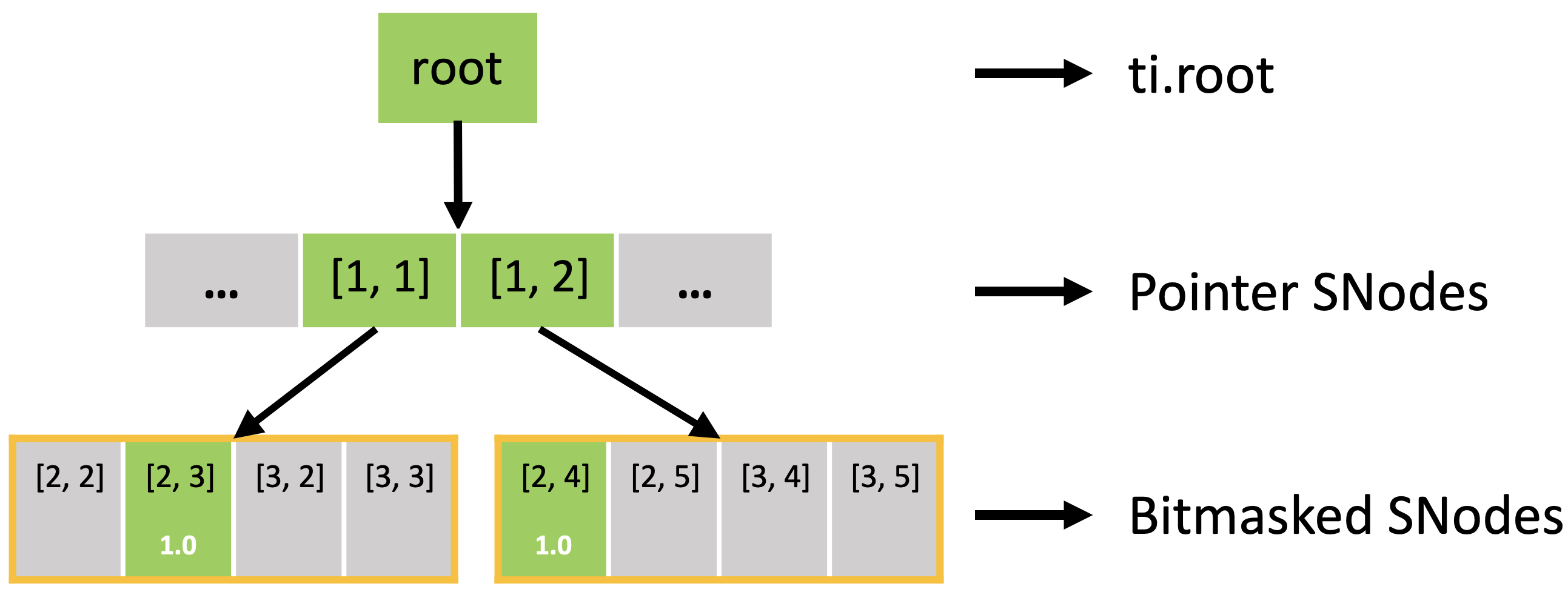
The code snippet below creates an 8x8 sparse grid, with the top-level being a 4x4 pointer array (line 2 of pointer.py), and each pointer pointing to a 2x2 dense block. Just as you do with a dense field, you can use indices to write and read the sparse field. The following figure shows the active blocks and pixels in green.
x = ti.field(ti.f32)
block = ti.root.pointer(ti.ij, (4,4))
pixel = block.dense(ti.ij, (2,2))
pixel.place(x)
@ti.kernel
def activate():
x[2,3] = 1.0
x[2,4] = 2.0
@ti.kernel
def print_active():
for i, j in block:
print("Active block", i, j)
# output: Active block 1 1
# Active block 1 2
for i, j in x:
print('field x[{}, {}] = {}'.format(i, j, x[i, j]))
# output: field x[2, 2] = 0.000000
# field x[2, 3] = 1.000000
# field x[3, 2] = 0.000000
# field x[3, 3] = 0.000000
# field x[2, 4] = 2.000000
# field x[2, 5] = 0.000000
# field x[3, 4] = 0.000000
# field x[3, 5] = 0.000000
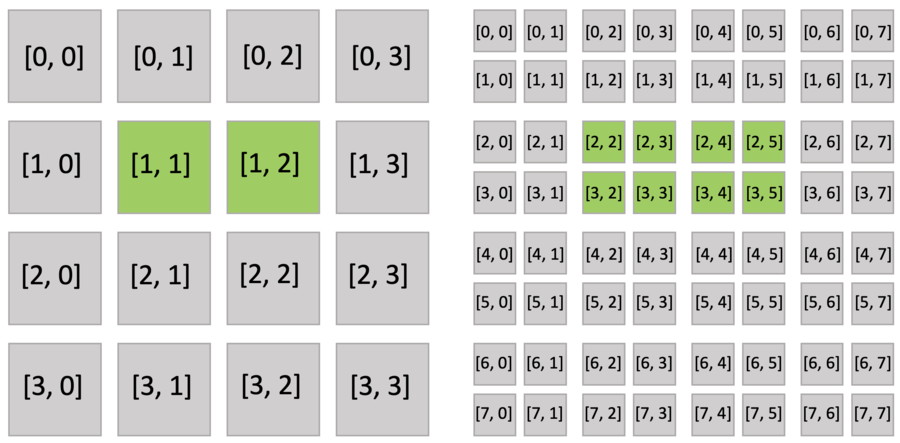
Executing the activate() function automatically activates block[1,1], which includes x[2,3], and block[1,2], which includes x[2,4]. Other pixels of block[1,1] (x[2,2], x[3,2], x[3,3]) and block[1,2] (x[2,5], x[3,4], x[3,5]) are also implicitly activated because all pixels in the dense block share the same activity value.
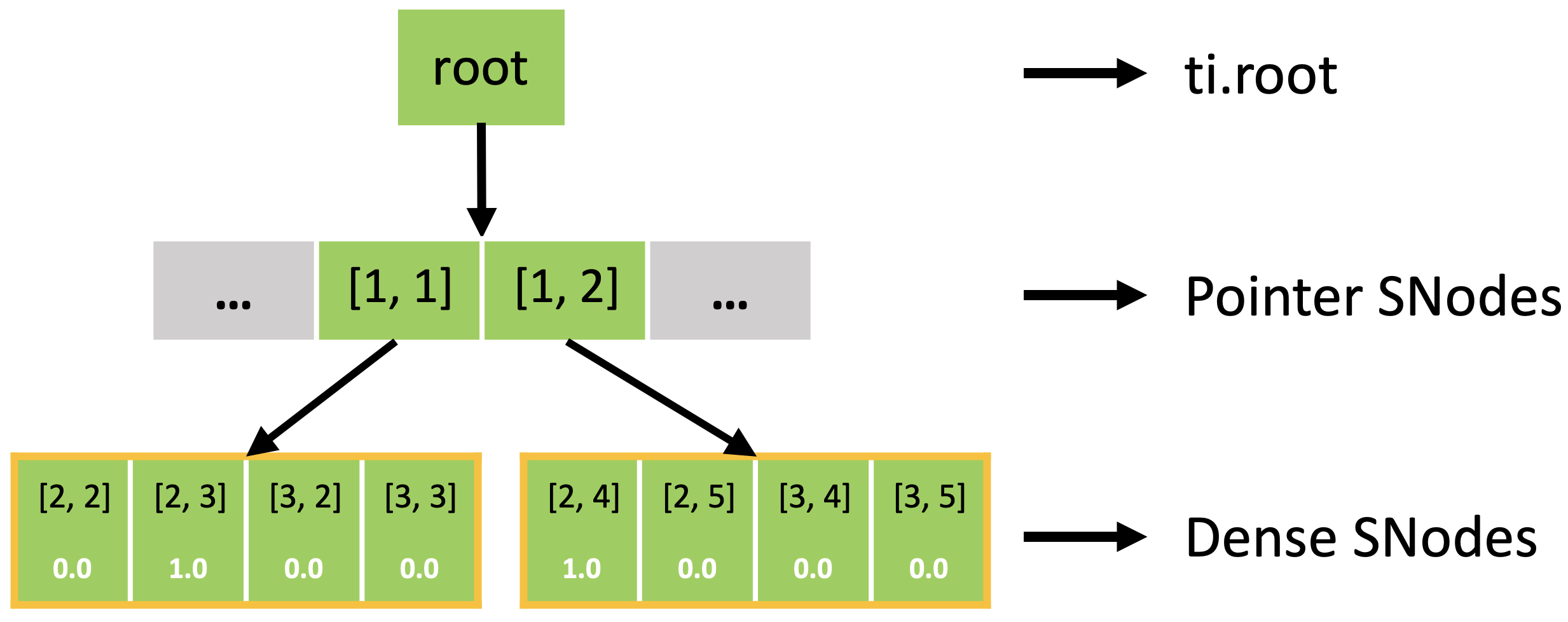
In fact, the sparse field is an SNode tree shown in the following figure. You can use a for loop to loop over the different levels of the SNode tree like the print_active() function in the previous example. A parallelized loop over a block for i, j in block would loop over all active pointer SNodes. A parallelized loop over a pixel for i, j in pixel would loop over all active dense SNodes.
Bitmasked SNode
While a null pointer can effectively represent an empty sub-tree, using 64 bits to represent the activity of a single pixel at the leaf level can consume too much space.
For example, if each pixel contains a single f32 value (4 bytes), the 64-bit pointer pointing to the value would take 8 bytes. The fact that storage costs of pointers are higher than the space to store the value themselves goes against our goal to use spatially sparse data structures to save space.
To amortize the storage cost of pointers, you could organize pixels in a blocked manner and let the pointers directly point to the blocks like the data structure defined in pointer.py.
One caveat of this design is that pixels in the same dense block can no longer change their activity flexibly. Instead, they share a single activity flag. To address this issue, the bitmasked SNode additionally allocates 1-bit per pixel data to represent the pixel activity.
The code snippet below illustrates this idea using a 8x8 grid. The only difference between bitmasked.py and pointer.py is that the bitmasked SNode replaces the dense SNode (line 3).
x = ti.field(ti.f32)
block = ti.root.pointer(ti.ij, (4,4))
pixel = block.bitmasked(ti.ij, (2,2))
pixel.place(x)
@ti.kernel
def activate():
x[2,3] = 1.0
x[2,4] = 2.0
@ti.kernel
def print_active():
for i, j in block:
print("Active block", i, j)
for i, j in x:
print('field x[{}, {}] = {}'.format(i, j, x[i, j]))
Furthermore, the active blocks are the same as pointer.py as shown below. However, the bitmasked pixels in the block are not all activated, because each of them has an activity value.
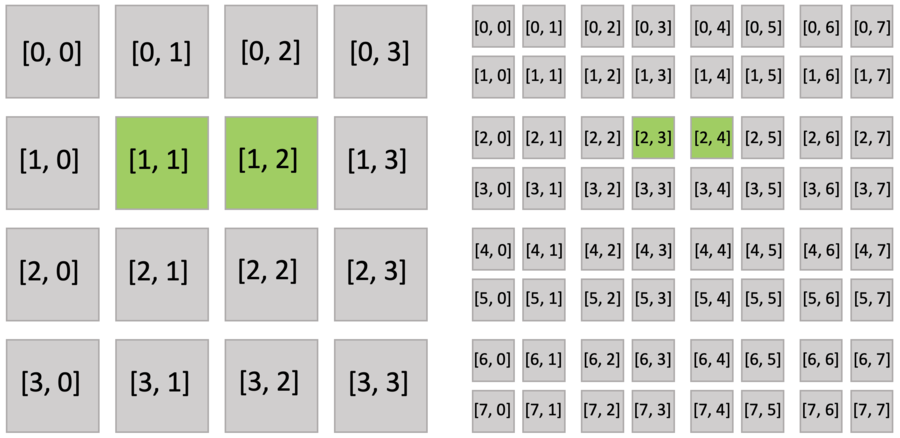
The bitmasked SNodes are like dense SNodes with auxiliary activity values.
Dynamic SNode
Taichi officially supports dynamic data structure Dynamic SNode since version v1.4.0. You can think of a dynamic SNode as a List that can only store data of a fixed type. The element types it supports include scalars, vectors/matrices, and structs. It also supports the following three APIs:
append: Dynamically adds an element, equivalent to theappendmethod of a Python list.deactivate: Clears all stored elements, equivalent to theclearmethod of a Python list.length: Gets the actual number of elements currently stored, equivalent to the__len__method of a Python list.
All three methods must be called inside the Taichi scope.
Unfortunately, Dynamic SNode does not support dynamically deleting elements like pop and remove. This is because it is difficult to implement these operations with high performance in parallel computing.
note
Here are a few rules you must obey when using Dynamic Snode:
Dynamic SNode can only be used in the CPU and CUDA backends.
A dynamic SNode must have one axis only, and the axis must be the last axis.
No other SNodes can be placed under a dynamic SNode. In other words, a dynamic SNode must be directly placed with a field.
Along the path from a dynamic SNode to the root of the SNode tree, other SNodes must not have the same axis as the dynamic SNode.
For example, to declare a one-dimensional dynamic list x that stores integers, we can write:
S = ti.root.dynamic(ti.i, 1024, chunk_size=32)
x = ti.field(int)
S.place(x)
Let's explain the meaning of these three lines of code:
- In the first line of code,
ti.root.dynamicmeans that the direct parent node ofSisti.root. Generally, callingS = P.dynamic()for an SNodePmeans the direct parent node ofSin the Snode tree isP. Hence this operation specifies the position ofSin the SNode tree system. - The first parameter of the
dynamicfunction is the axis on whichSis located. This axis must be one-dimensional and cannot have been used by any parent node ofS. Here we use the axisti.i(equivalent toaxis=0in NumPy). - The second parameter of the dynamic function is the maximum length of
S. Since Dynamic SNode dynamically allocates memory as needed, it does not occupy space when there is no data. However, this maximum length also has an upper limit (the maximum value of 32-bit int type), so it is not possible to assign an astronomical number to it at will. It is also possible to add elements beyond this maximum length, and elements outside the range can also be accessed normally using subscripts, but we recommend keeping the size of the list within the maximum length range. - The third parameter
chunk_sizewill be explained later in this article. - After obtaining the Dynamic SNode
Sin this way, we declare an integer field variablex = ti.field(int), and then callS.place(x)to convertxinto a data structure described byS. Before callingplace,xcannot be used to store data; after callingplace,xcan be used as a mutable list of typeint.
For example, we can use the append method to add data to x, and call the length function to get the actual length of x. Both functions must be called inside the kernel:
@ti.kernel
def add_data():
for i in range(1000):
x.append(i)
print(x.length())
add_data()
We can also call the deactivate method of x to clear the entire list, which is equivalent to restoring x to its uninitialized state:
@ti.kernel
def clear_data():
x.deactivate()
print(x.length()) # will print 0
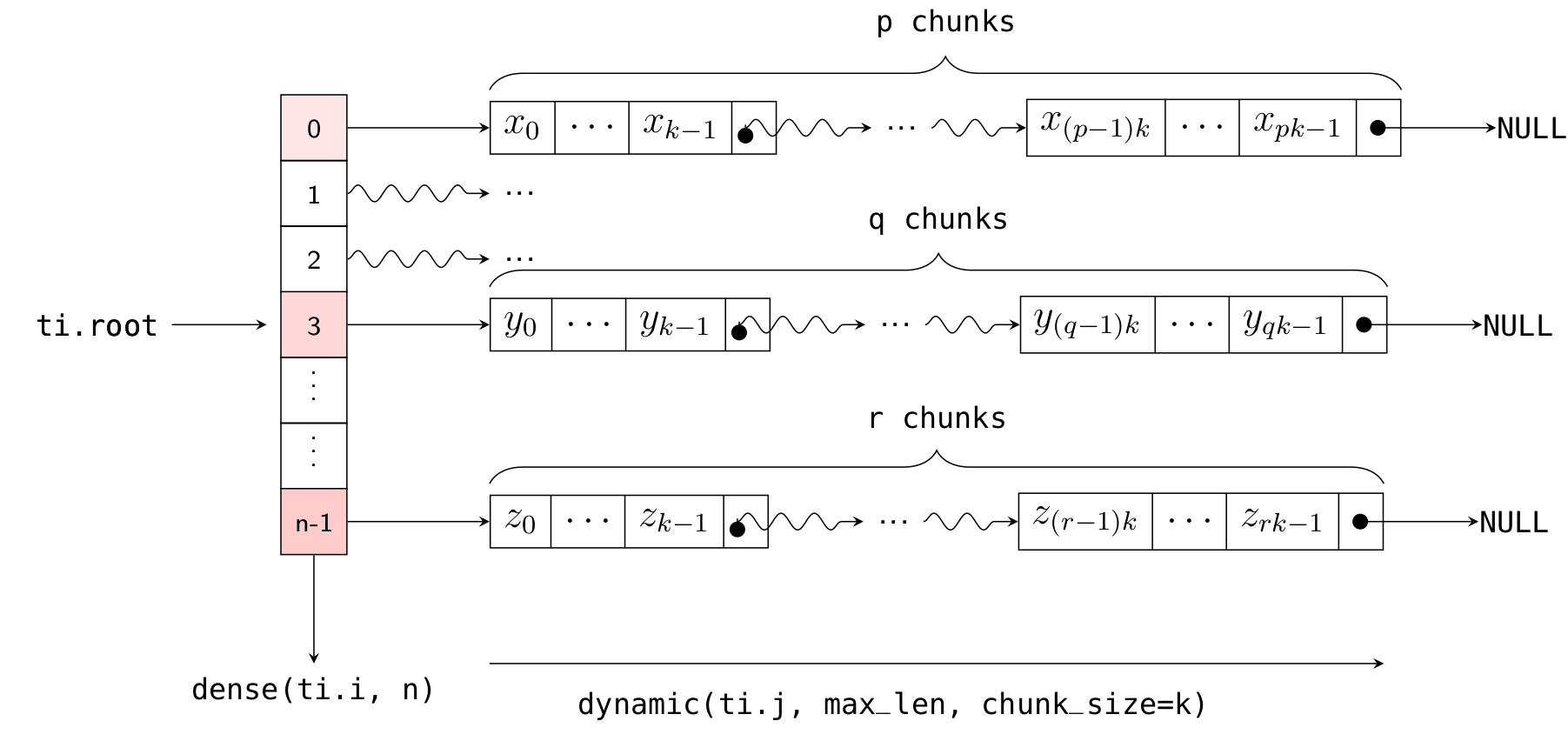
Returning to the explanation of the chunk_size parameter: the implementation of Dynamic SNode internally uses linked lists, where multiple elements are densely packed into a node (or "chunk") of the linked list, with each chunk containing chunk_size elements. Element allocation and deallocation are performed in units of chunks. The following diagram illustrates how x is laid out in memory (with k = 32):

Thus, the actual number of chunks allocated is ceil(x.length() / chunk_size).
We can also define more complex variable-length lists. For example, the following code defines an array x of length n = 10, where each element of x is a one-dimensional variable-length list:
S = ti.root.dense(ti.i, 10).dynamic(ti.j, 1024, chunk_size=32)
x = ti.field(int)
S.place(x)
Here, ti.root.dense(ti.i, 10) is a Dense SNode that represents a dense array of length 10 along the ti.i axis. S = ti.root.dense(ti.i, 10).dynamic(ti.j, ...) represents a child node of this Dense SNode, occupying the ti.j axis (which is different from the parent node!). The layout of x in memory is illustrated in the following diagram:
As with the one-dimensional case, you can dynamically add elements to the i-th list using x[i].append(), get the current length of the i-th list using x[i].length(), and clear the ith list using x[i].deactivate().
@ti.kernel
def add_data():
for i in range(10):
for j in range(i):
x[i].append(j)
print(x[i].length()) # will print i
for i in range(10):
x[i].deactivate()
print(x[i].length()) # will print 0
All of the above discussion applies to using Dynamic SNode with other numeric types. For vector/matrix and struct types, the steps are identical. For example, consider the following code using struct types:
S = ti.root.dynamic(ti.i, 1024, chunk_size=32)
SphereType = ti.types.struct(center=ti.math.vec3, radius=float)
x = SphereType.field()
S.place(x)
Here, x is a one-dimensional variable-length list that can store values of type SphereType.
Computation on spatially sparse data structures
Sparse struct-fors
Efficiently looping over sparse grid cells that distribute irregularly can be challenging, especially on parallel devices such as GPUs. In Taichi, for loops natively support spatially sparse data structures and only loop over currently active pixels with automatic efficient parallelization.
Explicitly manipulating and querying sparsity
Taichi also provides APIs that explicitly manipulate data structure sparsity. You can manually check the activity of a SNode, activate a SNode, or deactivate a SNode. We now illustrate these functions based on the field defined below.
x = ti.field(dtype=ti.i32)
block1 = ti.root.pointer(ti.ij, (3, 3))
block2 = block1.pointer(ti.ij, (2, 2))
pixel = block2.bitmasked(ti.ij, (2, 2))
pixel.place(x)
1. Activity checking
You can use ti.is_active(snode, [i, j, ...]) to explicitly query if snode[i, j, ...] is active or not.
@ti.kernel
def activity_checking(snode: ti.template(), i: ti.i32, j: ti.i32):
print(ti.is_active(snode, [i, j]))
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
activity_checking(block1, i, j)
for i in range(6):
for j in range(6):
activity_checking(block2, i, j)
for i in range(12):
for j in range(12):
activity_checking(pixel, i, j)
2. Activation
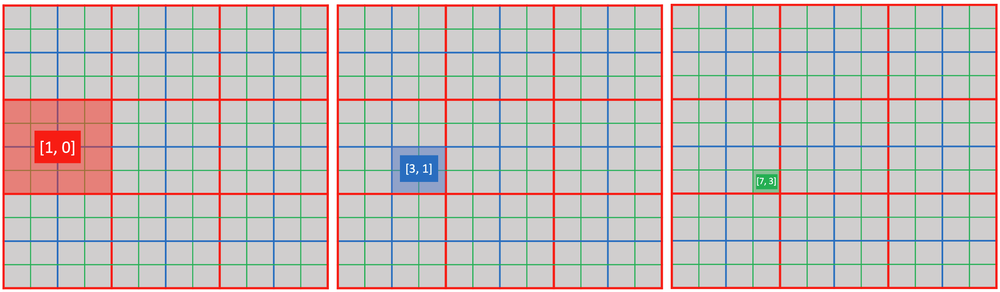
You can use ti.activate(snode, [i, j, ...]) to explicitly activate a cell of snode[i, j, ...].
@ti.kernel
def activate_snodes():
ti.activate(block1, [1, 0])
ti.activate(block2, [3, 1])
ti.activate(pixel, [7, 3])
activity_checking(block1, 1, 0) # output: 1
activity_checking(block2, 3, 1) # output: 1
activity_checking(pixel, 7, 3) # output: 1
3. Deactivation
- Use
ti.deactivate(snode, [i, j, ...])to explicitly deactivate a cell ofsnode[i, j, ...]. - Use
snode.deactivate_all()to deactivate all cells of SNodesnode. This operation also recursively deactivates all its children. - Use
ti.deactivate_all_snodes()to deactivate all cells of all SNodes with sparsity.
When deactivation happens, the Taichi runtime automatically recycles and zero-fills memory of the deactivated containers.
note
For performance reasons, ti.activate(snode, index) only activates snode[index]. The programmer must ensure that all ancestor containers of snode[index] is already active. Otherwise, this operation results in undefined behavior.
Similarly, ti.deactivate ...
- does not recursively deactivate all the descendants of a cell.
- does not trigger deactivation of its parent container, even if all the children of the parent container are deactivated.
4. Ancestor index query
You can use ti.rescale_index(descendant_snode/field, ancestor_snode, index) to compute the ancestor index given a descendant index.
print(ti.rescale_index(x, block1, ti.Vector([7, 3]))) # output: [1, 0]
print(ti.rescale_index(x, block2, [7, 3])) # output: [3, 1]
print(ti.rescale_index(x, pixel, [7, 3])) # output: [7, 3]
print(ti.rescale_index(block2, block1, [3, 1])) # output: [1, 0]
Regarding line 1, you can also compute the block1 index given pixel index [7, 3] as [7//2//2, 3//2//2]. However, doing so couples computation code with the internal configuration of data structures (in this case, the size of block1 containers). By using ti.rescale_index(), you can avoid hard-coding internal information of data structures.
Sparse grid
We now show an example of how to create a sparse grid with our simplified API(ti.sparse.grid()), and how to print the usage with ti.sparse.usage().
import taichi as ti
# create a 2D sparse grid
grid = ti.sparse.grid(
{
"pos": ti.math.vec2,
"mass": ti.f32,
"grid2particles": ti.types.vector(20, ti.i32),
},
shape=(10, 10),
)
# access
grid[0, 0].pos = ti.math.vec2(1, 2)
grid[0, 0].mass = 1.0
grid[0, 0].grid2particles[2] = 123
# print the usage of the sparse grid, which is in [0,1]
ti.sparse.usage(grid)
possible output:
Grid usage: 0.010000
Further reading
Please read the SIGGRAPH Asia 2019 paper or watch the associated introduction video with slides for more details on computation of spatially sparse data structures.
Taichi elements implement a high-performance MLS-MPM solver on Taichi sparse grids.